Sphinginae subfamily
Sphingini tribe:
 |
Agrius cingulata,
USGS Pink-spotted hawkmoth,
Larvae feed on plants in the Convolvulaceae family, especially
Ipomoea batatas (sweet potato) and in the Solanaceae family,
especially (Datura) (jimsonweed) and related plants in the
Americas. There is also a brown form. Look for very large, dark
spiracular circles. Very variable!
|
 |
Ceratomia amyntor
WO,
the Elm Sphinx or Four-horned Sphinx
Larvae feed on Elm (Ulmus), birch (Betula), basswood
(Tilia), and cherry (Prunus).
There are both green and brown forms. The four horns near
the head are diagnostic.generally more northerly distribution, unlikely.
|
 |
Young caterpillars feed gregariously on Catalpa species
(Catalpa bignoniodes and C. speciosa) in the
Bignoniaceae family, skeletonizing the foliage.
Larvae are mostly white in early instars.
|
 |
Fraxinus, Ligustrum, Quercus, Crataegus and
Chionanthus virginicus are listed as hosts.
In the fifth instar, the spiracular ovals are decidedly red and the
anal horn is off-white to pinkish laterally.
|
 |
Dolba hyloeus
WO, the Pawpaw Sphinx
Larvae feed on pawpaw (Asimina triloba), littleleaf sweetfern
(Myrica aspleniifolia), possum haw (Ilex decidua), and
inkberry (Ilex glabra) as well as Tall Gallberry Holly
(Ilex coriacea).
Louis Handfield reports larvae probably feed on Ilex verticellata
in Quebec.
|

|
Isoparce cupressi
WO, Cypress or Baldcypress Sphinx.
Larvae feed on needles of baldcypress (Taxodium distichum) at night and
pupate in shallow underground burrows where second generation
overwinters.
|
 |
Larvae feed upon various pine species, including loblolly pine
(Pinus taeda) and longleaf pine (P. pinaster). They are well
camouflaged and are without an anal horn.
|
 |
Larvae feed on ash in the Fraxinus genus. Syringa and Ulmus have
also been reported.
Note the black anal horn.
|
 |
The caterpillars are called Tomato Hornworms and each has a black horn at the end of the abdomen.
Larvae feed on potato, tobacco, tomato, and other plants in the
nightshade family (Solanaceae).
|
 |
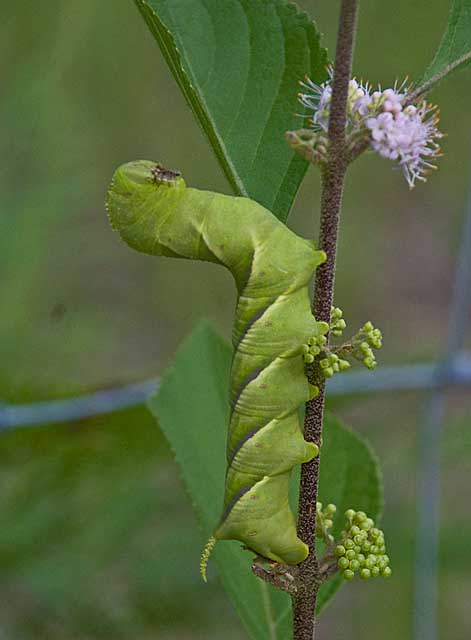
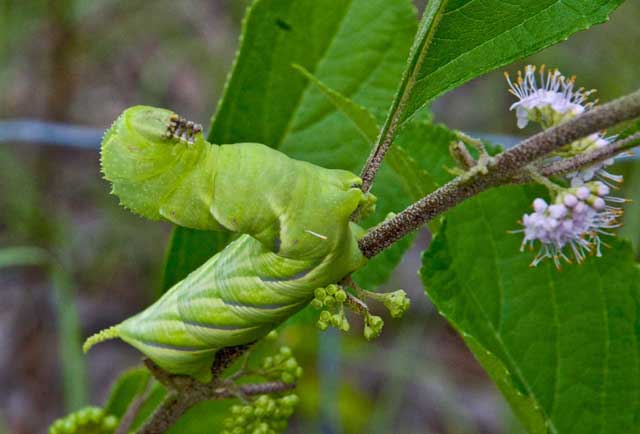
Manduca rustica
KDB, the Rustic Sphinx
The caterpillar has numerous white nodules on top of the thorax and
seven pairs of oblique, blue-gray stripes along the side of the body.
The horn is white at the base and blue-gray at the tip. Many hosts
are utilized.
|
Manduca rustica on beautyberry bush, July 28, 2008, Karen and Denny Beall
 |
Tobacco Hornworms, equipped with a red-tipped horn at the end of the
abdomen, are true gluttons and feed on tobacco and tomato, and
occasionally potato and pepper crops and other plants in the
nightshade family (Solanaceae).
|
 | Preferred hosts are common trumpetcreeper (Campsis radicans),
Florida yellow-trumpet (Tecoma stans), lilac
(Syringa species), and
passionflower (Passiflora species).
The anal horn is blue, preceded by a yellow dash.
|
 |
Larval hosts are apple (Malus), sweetfern (Myrica), Carolina rose
(Rosa carolina), blueberry and huckleberry (Vaccinium), white spruce
(Picea glauca), American larch (Larix laricina), and alder (Alnus).
|
Smerinthini Tribe:
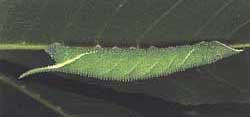 |
Amorpha juglandis larvae feed upon Walnut and butternut (Juglans),
hickory (Carya), alder (Alnus), beech (Fagus),
hazelnut (Corylus), and hop-hornbeam (Ostrya).
|
 |
Larvae accept willows, birches, and cherries.
I have also found them in the wild on oak in eastern Canada.
The skin is very granulose.
|
 |
The larvae depicted is probably third instar.
There may be more red spotting on the sides
as larvae mature.
|
 |
Larvae feed upon many forest trees including birches and cherries,
but are expecially fond of poplars and willows. Red markings on sides
vary greatly from specimen to specimen. generally more northerly; doubtful
|
 |
Protambulyx strigilis
WO,
the Streaked Sphinx:
In Florida larvae have been found on Schinus terebinthefolia.
Later instars hide at the base of a leaf or near the base of the
tree's trunk when not feeding (all larvae were found on saplings).
Early instar larvae have extremely pointed head capsules and sometimes have difficulty shedding their head capsules.
remote possibility
|
Macroglossinae subfamily
Dilophonotini tribe:

|
The body and wings are dark brown. The forewing has a large black
patch covering most of the outer half of the wing. There is a pale
tan cell spot (dark inner pupil), and a fairly straight median line
to the inside of the cell spot.
|
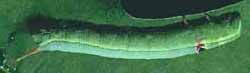 |
Erinnyis alope
WO, the Alope Sphinx.
Larvae have several forms and feed on papaya (Carica papaya),
nettlespurge (Jatropha), and allamanda (Allamanda).
|
 |
Larvae feed on papaya (Carica papaya), Cnidoscolus
angustidens, poinsettia (Euphorbia pulcherrima),
guava (Psidium species) and
saffron plum (Bumelia angustifolia/Bumelia celastrina).
Manilkara bahamensis,
Willow Bustic (Bumelia salicifolia)
and Painted Leaf (Poinsettia heterophylla) are also hosts.
Nice socks! Larvae show considerable variation.
|
 |
Erinnyis obscura, the Obscure Sphinx,
WO
Larvae feed on Rauvolfia ligustrina, Rauvolfia tetraphylla,
Stemmadenia obovata, Philibertia, Cynanchum, papaya
(Carica papaya), Asclepiadaceae, Blepharodon mucronatum,
White vine (Sarcostemma clausum) and Morrenia odorata.
rare
|
 |
Hemaris thysbe
WO, the Hummingbird Clearwing
There is also an orangey-pink prepupal form. The lateral line runs
from S1 to the blue horn.
Hemaris thysbe larvae feed on viburnum and related plants.
|
 |
Hemaris gracilis
WO, the
Slender Clearwing or Graceful Clearwing
Larval foods are blueberries including low bush blueberry
(Vaccinium vacillans), and laurel (Kalmia), all in the heath family
(Ericaceae).
|
Philampelini tribe:
 |
Larvae feed upon Grape (Vitis), Virginia Creeper
(Parthenocissus quinquefolia) and other vines and ivies
(Ampelopsis).
Larvae occur in both a light (green) form and a darker (tan/brown)
form. Note six "segmented" oblique lines.
|
 |
Eumorpha fasciatus
WO, the Banded Sphinx
Larvae feed upon primrose-willow, Ludwigia (water primrose)
and other plants in the evening primrose family. This hornless larva is
highly variable. Look for large, dark spiracular circles and a dark
line in the center of the back.
|
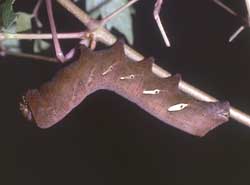 |
Eumorpha intermedia larvae feed upon peppervine, Ampelopsis arborea. Possibly they will also accept grape (Vitis species),
but so far no records of that host have been reported to my knowledge.
They like to remain well hidden within tangle of vines and probably feed mostly at night.
|
 |
There is a
striking resemblance to a snake's head and eye, and a flattening of
the thoracic segments when the head is not retracted.
In Florida larvae have been found on Possum Vine
(Cissus sicyoides).
Cissus incisa, Cissus verticillata, Eupatorium odoratum,
Ludwigia,
Magnolia, Parthenocissus and Vitis vinifera are all
reported hosts.
|
 |
If you have Grape or Virginia Creeper nearby, then you might encounter
this species. Note the five large white ovals. There are orangey-brown and green
forms also.
|
Macroglossini tribe:
 |
In additon to Virginia creeper larvae accept Grape (Vitis),
ampelopsis (Ampelopsis), and cayenne pepper (Capsicum).
Larvae are green until the final instar.
|
 |
Larvae feed on Azalea and Viburnum and progress very rapidly. The
larva to the left on Viburnum cassinoides is getting ready to
pupate. Color change from green to light burgundy-brown indicates
pupation is imminent. |
 |
Darapsa myron
WO, the Virginia Creeper Sphinx or the Grapevine Sphinx
If you have the
foodplants indicated in the common names, you probably have this
species nearby. The lower wings are orange.
Larvae feed on Virginia creeper (Parthenocissus quinquefolia),
Grape (Vitis), Ampelopsis, and Viburnum. |
 |
Larvae turn a deep chocolate brown just prior to pupation, and the
"horn" on the tail also turns downward as pupation draws near.
Darapsa versicolor larvae feed on Smooth hydrangea
(Hydrangea arborescens), buttonbush
(Cephalanthus occidentalis), and waterwillow
(Decodon verticillatus).
|
 |
Hyles lineata
USGS, the White-lined Sphinx
Larvae are highly varied and feed on a great diversity of plants
including willow weed (Epilobium), four o'clock (Mirabilis),
apple (Malus), evening primrose (Oenothera), elm
(Ulmus), grape (Vitis), tomato (Lycopersicon),
purslane (Portulaca), and Fuschia.
All larvae seem, however, to have the red/black swellings split by
dorso-lateral lines.
|
 |
Larvae also feed on Borreria, Catalpa and Manettia spp. and
Smooth buttonplant (Spermacoce glabra) and starclusters
(Pentas species). They are also recorded on joe-pie weed and
Hamelia patens and on Hedoydis nigricans. The green form may be more
common.
|
|
|



