Sphinginae subfamily
Sphingini tribe:
 | Salvia greggii has been confirmed as a larval host
by Robert A. Behrstock.
Jim Tuttle, tentative id, writes, "All of the
penultimate instars of both Lintneria (Sphinx) istar and
Lintneria (Sphinx) separatus that I have reared
have been mundane green."
|

|
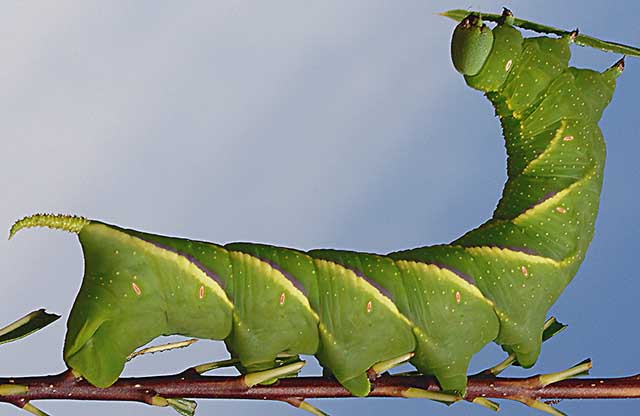
The caterpillars are called Tomato Hornworms and each has a black horn at the end of the abdomen.
Larvae feed on potato, tobacco, tomato, and other plants in the
nightshade family (Solanaceae). There is also a very beautiful brown form. See bottom of page.
|

|
The caterpillars are called Tomato Hornworms and each has a black horn at the end of the abdomen.
Larvae feed on potato, tobacco, tomato, and other plants in the
nightshade family (Solanaceae). There is also a very beautiful brown
form to the left.
|
 |
Manduca rustica
BB, the Rustic Sphinx
The caterpillar has numerous white nodules on top of the thorax and
seven pairs of oblique, blue-gray stripes along the side of the body.
The horn is white at the base and blue-gray at the tip. Many hosts
are utilized.
|
Manduca rustica,
Dog Canyon, on Desert Willow, (Chilopsis linearis), August 24, 2009, Bob Barber.
 |
Tobacco Hornworms, equipped with a red-tipped horn at the end of the
abdomen, are true gluttons and feed on tobacco and tomato, and
occasionally potato and pepper crops and other plants in the
nightshade family (Solanaceae).
|
 |
Larval hosts are unknown, but larvae probably feed on Lycium
in the nightshade family (Solanaceae).
Note the strong oblique black lines and the black anal horn.
|
 |
Larval hosts are Manzanita
and Arctostaphylos of the Ericaceae family.
Note the purple on both sides of the oblique white lines, the pale
blue horn, brown head and purple feet.
|
 |
The larvae are pale bluish green. The head has a pair of yellow
lateral bands meeting at the apex.
Larval hosts are ash, lilac, privet, cherry, and quaking aspen.
|
 | Larval hosts are Alligator juniper (Juniperus deppeana)
and other juniper species. It is amazing to me how well the larval
spiracular patches and false feet match
the pattern and colour of the juniper bark.
|
 | Larvae feed on New Mexican forestiera
(Forestiera neomexicana), on Forestiera angustifolia
and on little leaf ash (Fraxinus gooddingii) in the Oleaceae
family. There are green and dark forms and all larvae tend to darken
just before pupation.
|
 |
Sphinx vashti
USGS,
the Snowberry Sphinx
Larvae feed on the common snowberry (Symphoricarpos albus)
and on coralberry (S. orbiculatus). Note the two golden lines
of slightly raised bumps, one just behind the head, the other on the thorax.
questionable
|
Smerinthini Tribe:
 |
Larvae feed on cottonwood and poplar (Populus) and willow
(Salix). I suspect this species is the more likely of the two
Pachysphinx to fly in McKinley County.
Larvae are very chunky with little to distinguish them
from Pachysphinx modesta.
|
 |
Paonias myops
USGS,
the Small-eyed Sphinx
Wild cherry species are the favorites as larval
foodplants, but eggs will also be deposited on birches and other
forest trees. To the left a second/third instar larva rests on pin
cherry.
The "red heart" marking readily identifies this species.
|
 |
Smerinthus cerisyi
USGS,
Cerisy's Sphinx;
Cerisyi larvae greatly resemble modesta larvae, both being pale
green, with granular skin, pale lateral diagonal lines, faint red
spiracular circles, and very pale longitudinal lines running from the
head to a more pronounced anal diagonal line.
Larvae have green heads bounded dorsally with a pale yellow
inverted "V".
|
Macroglossinae subfamily
Dilophonotini tribe:
 |
Erinnyis obscura, the Obscure Sphinx,
WO
Larvae feed on Rauvolfia ligustrina, Rauvolfia tetraphylla,
Stemmadenia obovata, Philibertia, Cynanchum, papaya
(Carica papaya), Asclepiadaceae, Blepharodon mucronatum,
White vine (Sarcostemma clausum) and Morrenia odorata.
|
 |
Hemaris diffinis
WO, the
Snowberry Clearwing or Bumblebee Moth.
Larval host plants include Snowberry (Symphoricarpos),
honeysuckle (Lonicera), Coralberry, viburnums, Blue Dogbane
(Apocynum) and dwarf bush honeysuckle (Diervilla lonicera).
Horn is black with a yellow base. East of Great Divide.
|
 |
Larval host plants include Snowberry (Symphoricarpos),
honeysuckle (Lonicera), Coralberry, viburnums, high bush cranberry and hawthorn (Crataegus).
Horn is black with a slightly lighter base. This western species was formerly classified as
H. diffinis or H. senta. Those species west of the Continental Divide are now classified as
H. thetis.
|
Philampelini tribe:
 |
Larvae feed upon Grape (Vitis), Virginia Creeper
(Parthenocissus quinquefolia) and other vines and ivies
(Ampelopsis).
Larvae occur in both a light (green) form and a darker (tan/brown)
form. Note six "segmented" oblique lines.
|
Macroglossini tribe:
 |
Darapsa myron WO, the Virginia Creeper Sphinx or the Grapevine Sphinx
If you have the
foodplants indicated in the common names, you probably have this
species nearby. The lower wings are orange.
Larvae feed on Virginia creeper (Parthenocissus quinquefolia),
Grape (Vitis), Ampelopsis, and Viburnum. |

|
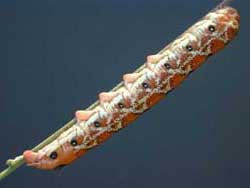
Hyles lineata
USGS, the White-lined Sphinx
Larvae are highly varied and feed on a great diversity of plants
including willow weed (Epilobium), four o'clock (Mirabilis),
apple (Malus), evening primrose (Oenothera), elm
(Ulmus), grape (Vitis), tomato (Lycopersicon),
purslane (Portulaca), and Fuschia.
All larvae seem, however, to have the red/black swellings split by
dorso-lateral lines. |
|
Larvae feed on (Onagraceae) including evening primrose
(Oenothera), gaura (Gaura), and willow weed
(Epilobium).
Early instars are green and lack the dark sharply contrasting
spiracular circles and other patterning.
|
 |
Larvae probably feed on (Onagraceae) including evening primrose
(Oenothera), gaura (Gaura), and willow weed
(Epilobium).
|
|
|

